# 基于 GA 遗传算法的智能组题模块的设计与应用
作者:南侠 (opens new window),编程导航星球 (opens new window) 编号 29240
基于 PyGad + Flask 的遗传算法实现的智能题单生成项目,根据题单题目难度分布、题目类型分布、受众能力等参数得到最优题目组合方案
在OJ系统中,题单生成是一个至关重要的环节。
一般来说,题单由多道题目组合而成,以满足特定需求,如受众能力、题型分布、难度比例和知识点分布等。
然而,传统的方法往往依赖于经验,通过筛选和组合题目来达到预期目标。
但这种方法存在时间成本高、误差率大的问题,对于新手来说尤其不友好。
因此,本文提出了一种新的思路:利用GA遗传算法来解决这一问题。通过将各种因素作为适应度函数的组成参数,在经过多次遗传进化操作后,最终得到相对最优的组合方案,给出题者提供优质的建议,以提高出题效率。
# (1)遗传算法简介和应用技术
遗传算法是受自然进化理论启发的一系列搜索算法。通过模仿自然选择和繁殖的过程,遗传算法可以为涉及搜索,优化和学习的各种问题提供高质量的解决方案。同时,它们类似于自然进化,因此可以克服传统搜索和优化算法遇到的一些障碍,尤其是对于具有大量参数和复杂数学表示形式的问题。
(Genetic Algorithm,简称GA)起源于对生物系统所进行的计算机模拟研究,是一种 随机全局搜索优化 方法,它模拟了自然选择和遗传中发生的 复制 、 交叉 (crossover)和变异 (mutation)等现象,从任一初始种群(Population)出发,通过随机选择、交叉和变异操作,产生一群更适合环境的个体,使群体进化到搜索空间中越来越好的区域,这样一代一代不断繁衍进化,最后收敛到一群最适应环境的个体(Individual),从而求得问题的优质解。
详细参考:https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/436453994
本文使用 PyGad 依赖库(版本:2.19.2),实现 GA 的代码实现,详情使用可参考以下链接:
- 官方文档:https://pygad.readthedocs.io/en/latest/pygad.html (opens new window)
- Demo使用:https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/385918911
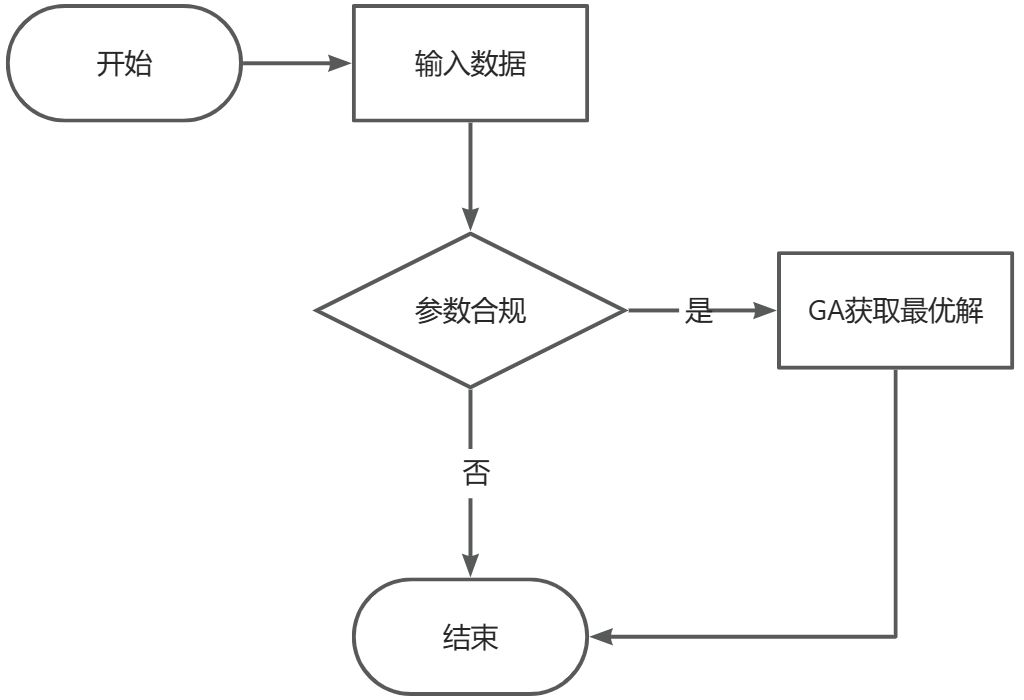
# (2)总体思路
# (3)适应度函数设计
# 1.输入数据
- questionRange:题目范围:List(index,Question)
- index:序列号,从0开始
- Question:题目信息对象
- id:题号(int)
- tags:知识点标签(list[str])
- questionDifficulty:难度类型(简单(0)、中等(1)、困难(2),int)
- questionType:题目类型(文字题(1)、编程题(0),int)
- popScore:受众评分(0-5,float)
- questionNum:题目数量(0,len(questionRange),int)
- needTags:所需知识点(至多5个,str)
- typeRate:题目类型比例(文字题:编程题=0:1,int)
- difficultyRate:题目难度比例(简单:中等:困难=0:1:2,int)
# 2.函数公式
在构建遗传算法的适应度函数时,我们需要考虑可选题目范围、受众评分、所需知识点、题目类型比例以及题目难度比例等多个因素。
适应度函数公式:
def max_fitness_function(solution, solution_idx):
# 根据solution索引数组获取题目信息数组
cur = [questionRange[e] for e in solution]
# 计算题目类型分布并归一化
type_distribution = calCurTypeRate(cur)
# 计算题目难度分布并归一化
difficulty_distribution = calCurDifficultyRate(cur)
# 计算题目受众分数
cur_popScore = calCurPopScore(difficulty_distribution)
# 计算适应度函数值(公式)
fitness = (
weight_popScore * (abs(popScore - cur_popScore) / popScore) +
weight_tags * calTagsLoss(cur) +
weight_typeRate * (abs(typeRate[0] - type_distribution[0]) + abs(typeRate[1] - type_distribution[1])) / 2 +
weight_difficultyRate * sum([abs(difficultyRate[i] - difficulty_distribution[i]) for i in range(3)]) / 3
)
return 1.0 / fitness
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
其中:
weight_popScore、weight_tags、weight_typeRate、weight_difficultyRate是权重系数,用于调整不同参数在适应度函数中的影响程度。这些系数可以根据实际需求进行调整。weight_popScore * (abs(popScore - cur_popScore) / popScore):受众评分的差异,表示题目与其受众分数和当前方案的受众分数的差距。calTagsLoss(cur):计算选取的题目中覆盖所需知识点的的比例。通过求交集并除以所需知识点数量(最多5个)来评估知识点覆盖情况。type_distribution:实际选取的题目类型分布比例,需要计算文字题和编程题各自在选取题目中的比例。(abs(typeRate[0] - type_distribution[0]) + abs(typeRate[1] - type_distribution[1])) / 2:计算实际题目类型分布与期望类型分布的差异,取平均值来得到类型分布的差异度。difficulty_distribution:实际选取的题目难度分布比例,需要计算三种难度在选取题目中的比例。sum([abs(difficultyRate[i] - difficulty_distribution[i]) for i in range(3)]):计算实际题目难度分布与期望难度分布的差异,取平均值来得到难度分布的差异度。
# (4)其余GA策略和参数
# pyGad参考链接:https://pygad.readthedocs.io/en/latest/pygad.html#pygad-ga-class
ga_instance = pygad.GA(
init_range_low=0, # 初始种群个体的基因最小值
init_range_high=len(questionRange) - 1, # 初始种群个体的基因最大值
num_generations=50, # 代数
num_parents_mating=20, # 要选择的父母解决方案数量
parent_selection_type="sss", # 选择策略(steady_state_selection:稳态选择:保证种群稳定性)
crossover_type="single_point", # 交叉策略(单点交叉:适用于二进制编码和实数编码等多种编码方式)
fitness_func=max_fitness_function, # 适应度函数
sol_per_pop=100, # 每一个种群中个体数量
num_genes=questionNum, # 染色体基因的数量
gene_type=int, # 基因值的数据类型
gene_space=range(0, len(questionRange)), # 基因值的取值范围
allow_duplicate_genes=False, # 是否允许染色体中存在重复的值
mutation_type="random", # 变异的类型:随机突变
mutation_percent_genes=5, # 基因变异的百分比概率
random_mutation_min_val=0, # 变异个体的基因最小值
random_mutation_max_val=len(questionRange) - 1 # 变异个体的基因最大值
)
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
# (5)完整代码
代码主要包括:
- GA 各部分的实例代码
- Flask 的网络接口开发代码
代码地址:https://gitee.com/sspuoj/sspuoj_ai_question_combine/tree/master/online
# (6)测试效果
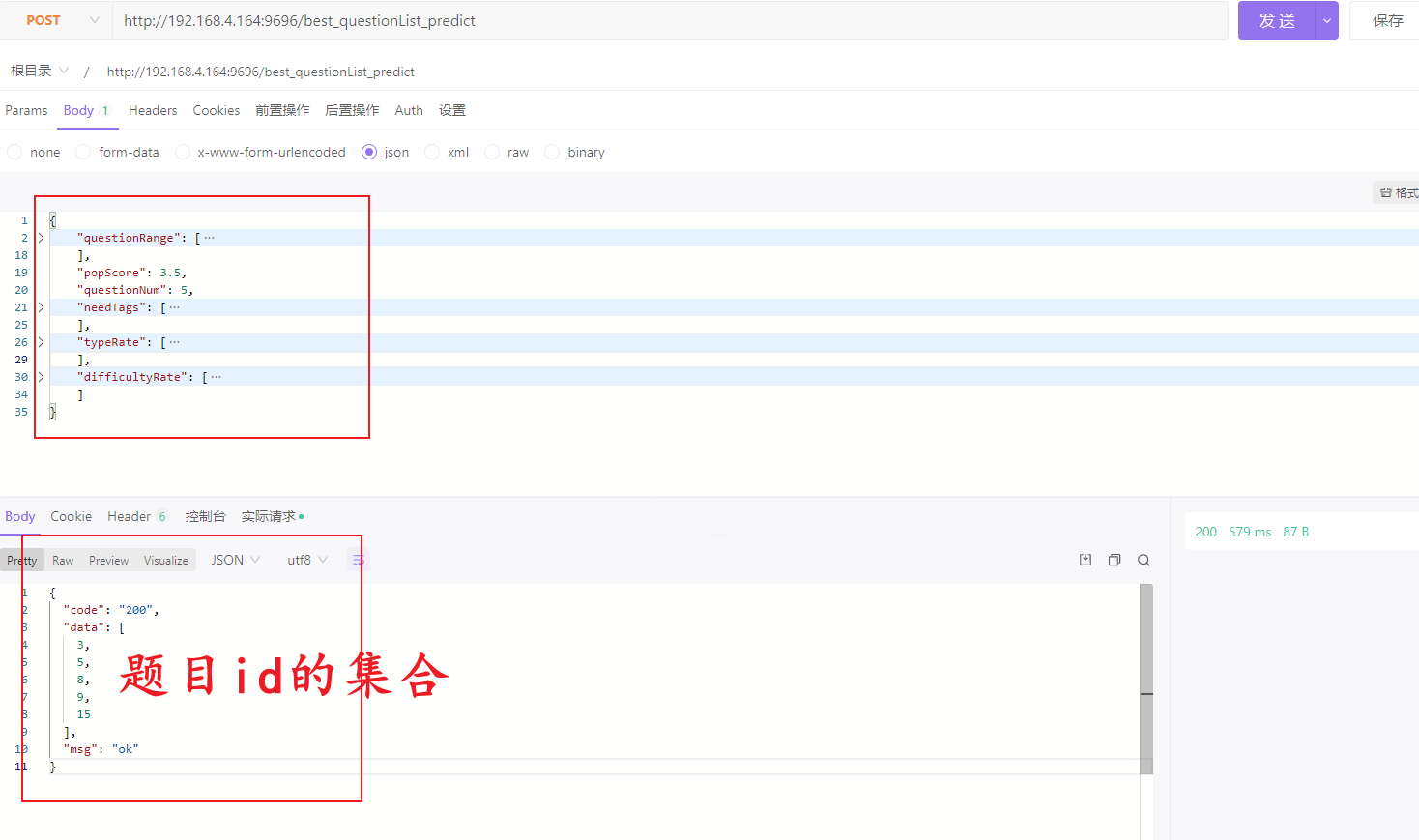
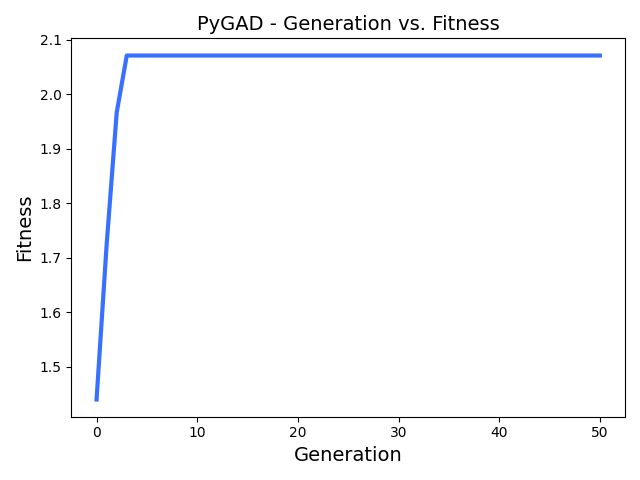
(GA的逐代优化过程变化图)

测试数据:
{
"questionRange": [
"{\"questionId\": 1,\"tags\": [\"迭代\", \"递归\"],\"questionType\": 0,\"questionDifficulty\": 0}",
"{\"questionId\": 2,\"tags\": [\"迭代\", \"DFS\"],\"questionType\": 0,\"questionDifficulty\": 0}",
"{\"questionId\": 3,\"tags\": [\"迭代\", \"BFS\"],\"questionType\": 1,\"questionDifficulty\": 1}",
"{\"questionId\": 4,\"tags\": [\"数学\", \"递归\"],\"questionType\": 1,\"questionDifficulty\": 1}",
"{\"questionId\": 5,\"tags\": [\"前缀和\", \"循环\"],\"questionType\": 0,\"questionDifficulty\": 2}",
"{\"questionId\": 6,\"tags\": [\"DFS\", \"递归\"],\"questionType\": 1,\"questionDifficulty\": 2}",
"{\"questionId\": 7,\"tags\": [\"BFS\", \"递归\"],\"questionType\": 1,\"questionDifficulty\": 0}",
"{\"questionId\": 8,\"tags\": [\"双指针\"],\"questionType\": 0,\"questionDifficulty\": 1}",
"{\"questionId\": 9,\"tags\": [\"迭代\"],\"questionType\": 0,\"questionDifficulty\": 2}",
"{\"questionId\": 10,\"tags\": [\"递归\"],\"questionType\": 0,\"questionDifficulty\": 2}",
"{\"questionId\": 11,\"tags\": [\"迭代\", \"递归\"],\"questionType\": 1,\"questionDifficulty\": 1}",
"{\"questionId\": 12,\"tags\": [\"迭代\", \"DFS\"],\"questionType\": 1,\"questionDifficulty\": 1}",
"{\"questionId\": 13,\"tags\": [\"迭代\", \"递归\",\"DFS\"],\"questionType\": 1,\"questionDifficulty\": 0}",
"{\"questionId\": 14,\"tags\": [\"迭代\", \"递归\",\"BFS\"],\"questionType\": 1,\"questionDifficulty\": 0}",
"{\"questionId\": 15,\"tags\": [\"迭代\", \"递归\",\"AVL\"],\"questionType\": 1,\"questionDifficulty\": 0}"
],
"popScore": 3.5,
"questionNum": 5,
"needTags": [
"DFS",
"BFS",
"递归"
],
"typeRate": [
0.3,
0.7
],
"difficultyRate": [
0.2,
0.5,
0.3
]
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35